IoT solutions
The Internet of things (IoT) is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
Our goal is to provide the market with systems, services and products which enable better optimization and modernization of processes and lower costs. We accept challenges as a chance to gain new knowledge and enrich our experiences.
We are flexible, we keep learning and growing which allows us to take on more and more difficult tasks because we know how, we want to and we can!
A universal solution in the field of automation and informatization of systems that would fit every company does not exist. That’s why we offer tailored solutions which enable a better optimization and modernization of processes which leads to a higher competitive advantage of our partners on the market.
iIoT - Industry 4.0
The Industrial Internet of Things (iIoT), which is also known as Industry 4.0 when applied to the manufacturing industry, is a concept of integrating smart manufacturing machinery, AI-powered automation, and advanced analytics to help make every worker and every factory more efficient.

IoT Buildings - Smart Buildings
Use IoT data to make informed decisions to optimize the experience of occupants, staff and management. With asset optimization, better facilities management and occupant safety, smarter buildings can streamline business processes and expand profits.

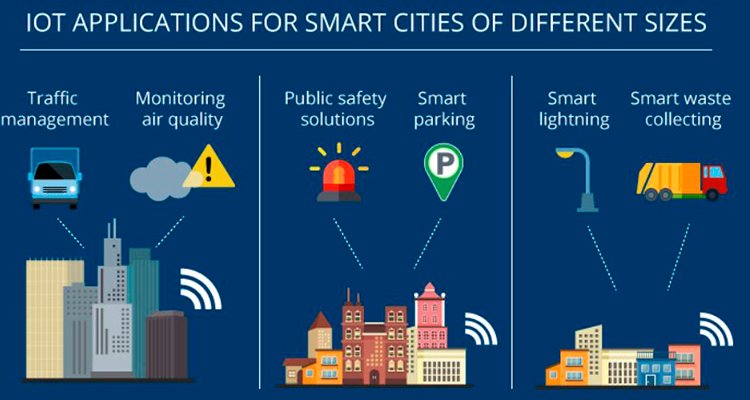
IoT Smart City
Smart cities use IoT devices such as connected sensors, lights, and meters to collect and analyze data. The cities then use this data to improve infrastructure, public utilities and services, and more. Today's most common smart city applications are utility metering, street and traffic lighting, traffic tracking and management, parking, road pricing, waste management, environmental monitoring and payment processing. At Linx, we develop the versatile components needed to transform the way you operate your Smart City. We focus on technologies that enable the Smart City to reduce waste, minimize operating costs, and improve quality of life.
Utility metering
Smart meters allow you to capture and transmit electricity, gas and water usage data, as well as performance, failure and blackout information in real time and remotely, thereby saving the need for a technician to come out to inspect equipment.
Street lighting
By making street lights “smart,” you can gain considerable savings in cost and environmental resources. Place sensors (Zhaga or NEMA) in adaptive street lights and you can transmit data about environmental conditions to control when lights turn on / off and how brightly they shine. For example, on a foggy day, lights could come on earlier than originally programmed. Also, in more remote areas, lights could brighten up from a dimmed power savings mode only when traffic is approaching.
Parking, road pricing & traffic management
Reducing traffic congestion, avoiding hazards, or simply making it easier to drive directly to a free parking spot, smart traffic management benefits drivers, passengers and everyone around them. Further, automatic payment of parking fees and road tolls provides greater convenience for individuals and reduces costs for operators. In all those use cases, smart sensors are deployed to transmit status data which in turn can be relayed to drivers, as well as provide Smart City authorities with vital information about the usage and flow of people and resources.
Waste management & environmental monitoring
To improve your city's environmental footprint, smart sensors connected via wireless technologies can monitor the status of your city's air quality and pollution levels, reporting critical information in real time. With connected smart sensors in waste bins, you can monitor fill levels and thus optimize the routes of waste collection vehicles to lower emissions, save fuel costs and reduce vehicle wear and tear. Using all the collected data, you can develop plans and strategies to improve the environmental wellbeing of your Smart City.